Equality and Inequality of Temperature | Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics | Gas Thermometer
Equality of Temperature
Two systems are said to have equal temperature if no change would occur in either system when they brought into contact with each other. Consider system A fitted with pressure gauge. If there is no change in pressure if it is brought into contact with other system B, then the two systems are said to have the same temperature. In other words, two systems have equality of temperature when no change in any observable property occurs when they are in contact.
Zeroth Law
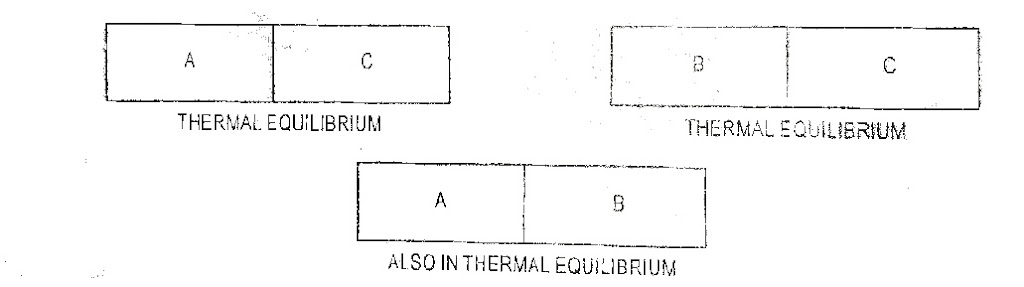
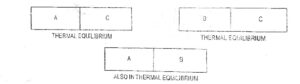
If the two systems are at same temperature, then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium. The principle of thermal equilibrium is stated in the form of law which is called zeroth law of thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics states that if two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system they are also in equilibrium with each other.
 |
| Fig.1 Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics |
If the systems A and B are in thermal equilibrium with system C then A and B must be in equilibrium with each other. It implies that if two systems each have the same temperature as a third system, they have the same temperature on each other.
The concepts of equality of temperature provide the possibility of devising a scale or means of measuring temperature. The temperature of any system S may be compared by bringing a thermometer into contact with system. The temperature of S is function of the length of a column of mercury in the thermometer.
Inequality of temperature
Consider the system A has contacted with B until it has reached equilibrium with B. At this condition, the temperature of A and B are equal. If A is removed and brought into contact with another system C, and an observable changes do take place in A. Thus the temperature of A and C are said to be unequal. In other words the system A and C have inequality of temperatures.
The system A must be selected such that changes in its physical properties are easily observed. The most common choice is the mercury in a glass capillary tube. The change in volume of mercury relative to the glass in readily seen.
Triple point
At the tenth conference on weights and measures in 1954, the Celsius scale was redefined using one fixed point where ice, water and vapour are coexist in equilibrium. This fixed point is called triple point. Temperature at triple point(Tt) is arbitrarily assigned the value of 273.16 K(0.01°C + 273.15) and is related with the equation.
Tt = a.x1
where x1 = thermometric property
a = Tt/xt = 273.16/xt
Consider a body whose temperature (T) to be measured is placed in contact with at its triple point, it follows that
T = ax = (273.16/xt).X
T = 273.16 × (x/xt)
or T/Tt = x/xt, where subscript, t refers to triple point of water.
Gas thermometer :
Thermometer devices are based on the assumption that temperature change is directly proportional to change in the property that is measured by the device. Temperature vary almost linearly with pressure and volume of permanent gases (gases that are difficult to liquefy). Hence gases, particularly hydrogen and helium are used for accurate measurement of temperature in a constant volume or constant pressure gas thermometer. The constant volume gas the thermometer is simple in construction and easier to operate.
Advantages of gases over liquids :
The main advantages of gases over liquids as a thermometer substance are are :
- For same rise in temperature gases expand more than liquid and lead to a negligible correction.
- Gases are more sensitive to gain or loss of heat. Thus they have very low specific heat than the liquid.
- The scales furnished by different gases are nearly identical
Constant-Volume Gas Thermometer :
Permanent gases may be used to define temperature scales which agree closely with absolute scales of temperature. The constant volume Gas thermometer is shown schematically in Fig.2. A capillary tube connects glass bulb containing a small quantity of gas with U-tube manometer.
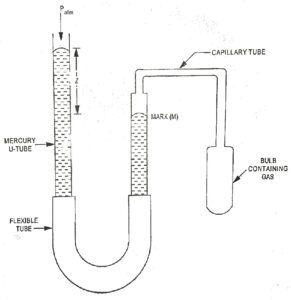 |
| Fig.2 Constant Volume Gas Thermometer |
The other name of U-tube ab to atmosphere. It can be moved vertically to adjust the Mercury level so that the Mercury just touches the mark (M) on capillary tube. The pressure in the bulb is used as a thermometric property and is given by the equation.
p = patm + ρm.g.z
Where patm = atmospheric pressure
ρm = density of mercury
The pressure measurement is made with the bulb in contact with the body whose temperature is to be measured.
In a constant pressure gas thermometer the volume of gases is considered as thermometric property and the mercury level is adjusted to keep z constant.
Ideal Gas Temperature :
The readings of a constant volume Gas thermometer depend upon the nature of gas. However, all gases indicates same temperature as pt is lowered and made approach to zero.
Consider p be the pressure of gas steam. Then its temperature (T) can be related by the equation.
T/Tt = p/pt
or T = 273.16 (p/pt) = 273.16 (p/1000)
where pt = pressure of gas at triple point of water and is equivalent to 1000 mm Hg.
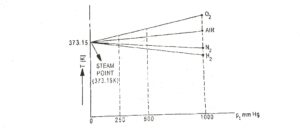 |
| Fig.3 Ideal Gas Temperature for Steam Point |
Now remove certain amount of gas from the bulb, such that pt is reduced to 500 mm Hg. Determine the new value of p, then T for steam. considering at 1 atm is related by the equation.
T = (273.16 p)/500
Repeat the procedure withdrawing more and more gas from the bulb so that pt decreases steadily, and at each value of pt calculate T.
Present the data in the form of T versus pt graph. Read the value of T from the graph when lim pt→ 0. The graph (Fig.3) illustates that all gases indicate the same temperature as pt is lowered and made to approach zero.
To measure the temperature other than at steam point the following equation may be used.
T/Tt = lim pt→0 (p/pt)
or T = 273.16 lim pt→0 (p/pt)
Temperature calculated by using above equation is called ideal gas temperature and the particular temperature scale is referred as ideal gas temperature scale.