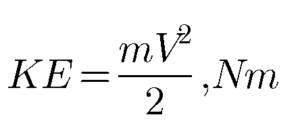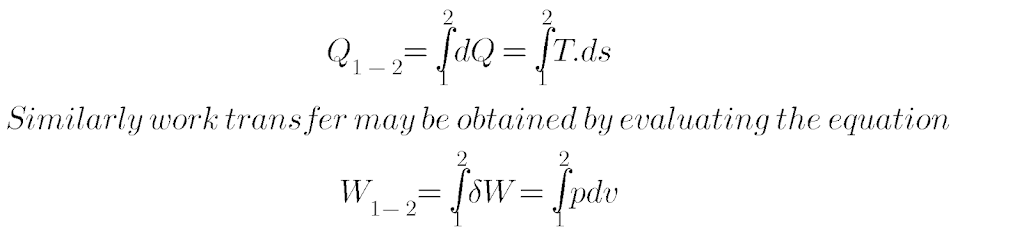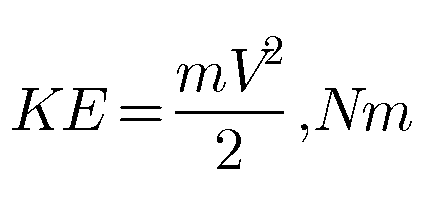
Stored energy is the energy possessed by a system. Stored energy in the system is called energy in a state. It is associated with a state. It change depends only on the end states of the process and not on the path of the process. In a cyclic process the net change in stored energy of a system is zero.
The types of energies encountered in engineering situations are Potential Energy (PE), Kinetic Energy (KE) and Internal Energy (U). For a system that contains only a compressible substance, the total energy (E) is given by the equation
E = PE + KE + U
When the system is stationary and effect of gravity is neglected then PE = 0 , and KE = 0. In such cases
E = U
The Stored energy which is a function of elevation is called potential energy suppose a system has a mass m and and elevation z above the reference line then the potential energy of a system is given by the equation
PE = mgz, Nm
he stored energy which is a function of velocity of the mass of the system is called Kinetic energy. Suppose a system has a mass of m and a velocity V then the kinetic energy of a system is given by the equation
Internal energy is the molecular energy possessed by a substance or system. Internal energy of a system is due to motion (translation rotation and vibration) of molecules. The change of internal energy depends upon the change in temperature of the system.
In otherwords
It is the heat energy stored in a gas. If a certain amount of heat is supplied to a gas the result is that temperature of gas may increase or volume of gas may crease thereby doing some external work or both temperature and volume increases; but it will be decided by the conditions under which the gas is supplied heat. if during heating of the gas the temperature increases its internal energy will also increase.
Joule’s law of internal energy states that internal energy of a perfect gas is a function of temperature only. In other words internal energy of a gas is dependent on the temperature change only and is not affected by the change in pressure and volume. We do not know how to find the absolute quantity of internal energy in any substance; however, what is needed in engineering is the change of internal energy (∆U).
The energy in a state is a property of a system and depends on the end States only not on a process. The properties of a system are point functions and are called exact differentials. Therefore the change in any properties can be represented as
dU = U₂− U₁
The energy in transition such as heat and work are path functions. When a system changes from state 1 to state 2 their change (change in properties) depend upon the process i.e., the path followed by the system therefore they are inexact differentials .
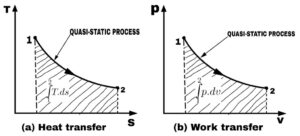
Thus heat is an inexact Differential and is written as δQ. When the system changes from state 1 to state 2, the quantity of heat transfer may be obtained by evaluating the equation