Ordered Pairs and Equality of an Ordered Pairs
Ordered pairs
An ordered pairs consists of two objects or elements in a given fixed order.
An ordered pairs consists of two objects or elements in a given fixed order.
Introduction about thermodynamics Energy is the capacity to do work energy cannot be created or destroyed but only can be changed into other forms (principle of conservation of energy). Thermodynamics mainly deals with interaction between heat and work (mechanical energy) and change in the property is associated with these interactions. The interaction between heat and…
Difference of sets Let A and B be two sets. The difference of A and B written as A – B, is the set of all those elements of A which do not belong to set B Thus A – B={ x : x ∈ A and x ∉ B} or A – B={ x…
Subsets of the set R of real numbers Following sets are important subsets of the set R of all real numbers: (i) The set of all natural numbers N = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,…. } (u) The set of all integers Z = { … – 3, – 2, -1,…
Open interval If a and b are two real numbers such that a < b, then the set of all real numbers x satisfying a x b is called an open interval and is denoted by (a, b) or ]a, b[ . Thus, (a,b) = (x: x ∈ R, a < x < b).
Ideal gases The term gas is applied to a particular phase of a pure substance which will fills the system boundary, and no change of phase takes place or is contemplated. They always exist in gaseous form. For this reason, they have been called permanent gases. Perfect…
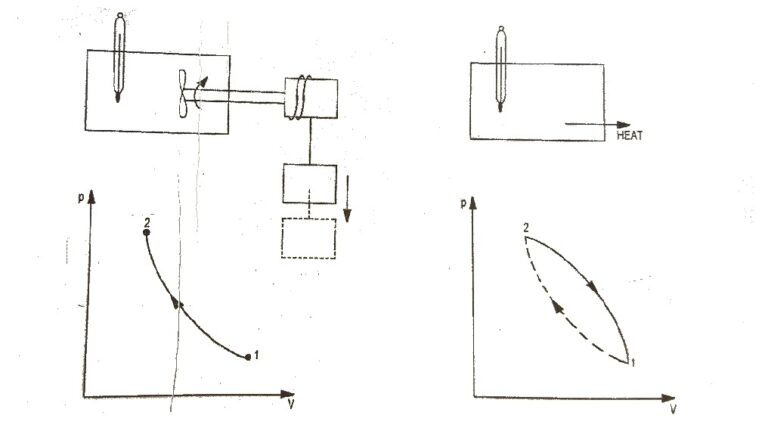
First Law of a Closed System Undergoing a Cycle : The first law of thermodynamics states that during any cycle a system undergoes the cyclic integral of heat is equal to the cyclic integral of the work. Fig.1 First Law of Thermodynamics To illustrates this, consider the gas as a system in…