Symmetry Difference of Sets
Symmetry difference of sets
| Fig (9) |
| Fig (9) |
Disjoint sets Two sets A and B are said to be disjoint, if A∩B=Φ. If A∩B≠Φ, then A and B are said to be intersecting or overlapping sets As shown in Fig(vi) Fig(vi) Example If A={ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }, B={ 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 } and C= { 6, 8, 10,…
Ideal gases The term gas is applied to a particular phase of a pure substance which will fills the system boundary, and no change of phase takes place or is contemplated. They always exist in gaseous form. For this reason, they have been called permanent gases. Perfect…
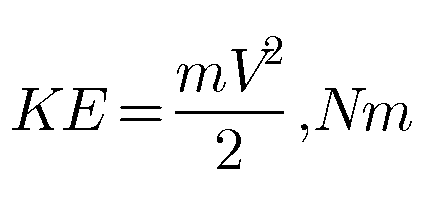
Energy in a state Stored energy is the energy possessed by a system. Stored energy in the system is called energy in a state. It is associated with a state. It change depends only on the end states of the process and not on the path of…
Intervals as subsets of R Closed intervals Let a and b be two given real numbers such that a < b. Then the set of all real numbers x such that a ≤ x ≤ b is called a closed interval and is denoted by [a, b] . Thus, [a, b] = {…
Laws of algebra of set THEOREM 1 (Idempotent Laws) For any set A (i) A ∪ A = A (ii) A ∩ A = A PROOF (i) A ∪ A= { x : x ∈ A or x ∈ A} ={x : x ∈ A} = A (ii) A ∩ A = {x : x…
Conservation of Energy In the early part of 19th century the scientist developed the concept of energy and hypothesis that it can be neither created nor destroyed ; this come to be known as the law of the conservation of energy. The first law of thermodynamics is merely one statement of this…