Thermodynamic system
Thermodynamic system is defined as quantity of matter or a region in a space chosen for study. Everything external to the system is called surroundings. The system is separated from the surroundings by the boundary that may be real or imaginary
The boundary does not intervene between the system and surroundings. It only allows the transfer of mass or energy between them
Universe:
A system and its surroundings together comprise of universe figure1 shows the conventional representation of a system
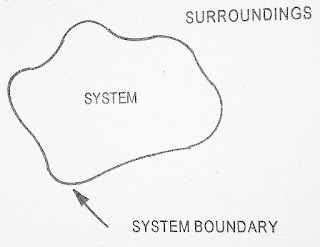 |
| Fig.1.1 Thermodynamic System |
Classification of systems
Thermodynamic systems are classified as
-
Closed system 2) Open system
3) isolated system
Closed system
Closed system is a system of fixed mass. The Mask and not across the boundary of the system but there may be transfer of energy into or out of the system. The gas contained in a cylinder-Piston arrangement constitute a closed system.
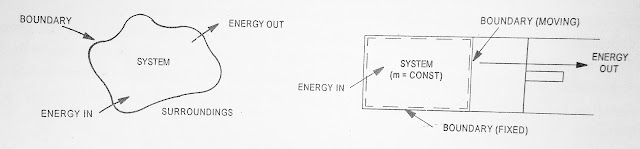 |
| Fig.1.2 Closed System |
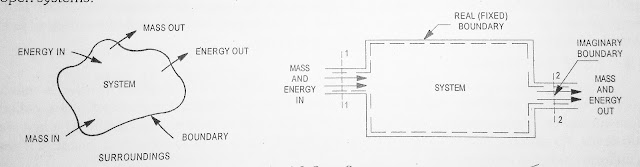
Open system:
Open system is one in which both mass and energy can across the boundary of the system. Most of the engineering devices such as nozzle, diffuser, compression or turbine are open systems.
 |
| Fig.1.3 Open System |
Isolated system :
Isolated system is one in which there is no mass or energy transfer across the system boundary. Thus in isolated system there is no interaction between the system and surroundings. A pan and containing hot water kept in an insulated box, is an example of an isolated system.
 |
| Fig.1.4 Isolated System |
Control volume:
In open system besides the energy there is a flow of mass into and out of the system. The selected region within the space i.e, portion of volume considered for thermodynamics analysis is called control volume and the boundary of control volume is called control surface. There is a flow of energy as well as mass into and out of the control volume but the shape of control volume will remain unchanged. A control volume and control surface is illustrated in Figure 1.5.
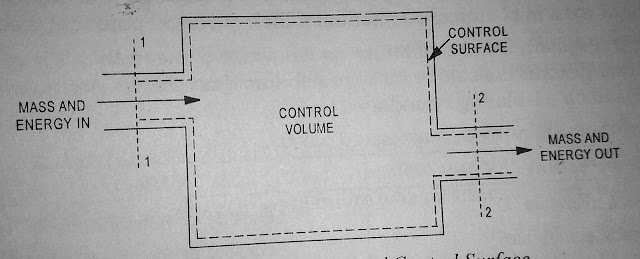 |
| Fig.1.5 Control Volume |
Comparison between control volume and system
The control volume and system are defined by boundaries. They permit the instructions across the boundaries which are related to the changes occurring within them. These features are common in both the concepts. However these concepts are distinguished by the following features.
-
the system boundary may change shape position and orientation relative to the observer while control-volume boundary does not change.
-
Material may flow across the control volume boundary but no such file or text place across a system boundary.
Because of these similarities and distinctions the control volume and system or equivalent to the open system and closed system respectively.
Homogeneous and heterogeneous systems
Homogeneous portion of a matter is called phase. A system with same chemical composition and uniform physical structure throughout its mass is called homogeneous system, and it exist in a single phase while a system consisting of different chemical composition is called heterogeneous system. Heterogeneous system exist in more than one phase.