Intersection of Sets
Intersection of sets
| Fig(v) |
| Fig(v) |
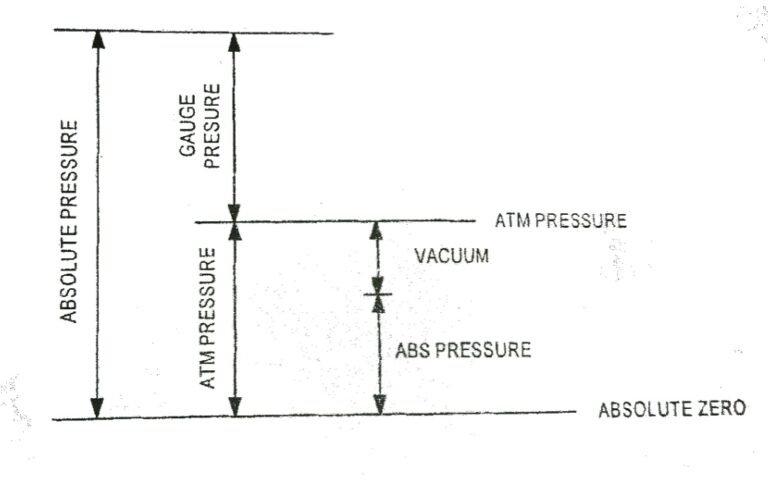
Pressure The molecules of a gas are in random motion. The rapidly moving molecules continually impact on the surface of the container and its effect is to produce a force over the surface. The force normal to unit area of surface is called pressure acting on the surface. The normal force exerted by the atmosphere…
Symmetry difference of sets Let A and B be two sets. The symmetry difference of sets A and B is the set (A-B) ∪ (B-A) and it is denoted by A ∆ B. Then A∆B=(A-B) ∪ (B-A) = {x : x ∉ A ∩ B}. In Fig 9 shaded region represents A∆B Fig (9) Example…
Theorem 3 The total number of subsets of a finite set containing n elements is 2ⁿ. Proof Let A be a finite set containing n elements.Let 0 ≤ r ≤ n. Consider those subset,of A that have r elements each.We know that the number of ways in which r elements can be chosen…
Universal set In any discussion in set theory, there always happens to be a set that contains all sets under consideration i.e. it is a super set of each of the given sets. Such a set is called the universal set and is denoted by U. Thus a set that contains all sets in a…
Laws of algebra of set THEOREM 1 (Idempotent Laws) For any set A (i) A ∪ A = A (ii) A ∩ A = A PROOF (i) A ∪ A= { x : x ∈ A or x ∈ A} ={x : x ∈ A} = A (ii) A ∩ A = {x : x…
Relation Let A and B be two sets. Then a relation from set A to B is a subset of A × B. Thus, R is a relation from A to B⇔R ⊆ A × B. If R is a relation from a non-void set A to non-void set B and my if (a, b)…