Function as a Machine
Function as a machine
 |
| Fig. 2(b) |
 |
| Fig. 2(b) |
First Law for a Closed System Undergoing a Quasi-static process In many occasions it is necessary to consider a system undergoing a process rather than a cycle. The equation, ∮ dQ − ∮ dW = 0 is applicable during the system undergoing a cycle, and algebraic sum of all energies transfer across the system boundary…
Conservation of Energy In the early part of 19th century the scientist developed the concept of energy and hypothesis that it can be neither created nor destroyed ; this come to be known as the law of the conservation of energy. The first law of thermodynamics is merely one statement of this…
Thermodynamic system Thermodynamic system is defined as quantity of matter or a region in a space chosen for study. Everything external to the system is called surroundings. The system is separated from the surroundings by the boundary that may be real or imaginary The boundary does not intervene between the system and surroundings. It only…
Union of sets Let A and B be two sets. The union of A and B is the set of all those elements which belong either to A or to B or to both A and B. We denote A union B by notation “A ∪ B” Thus A∪B = { x : x ∈…
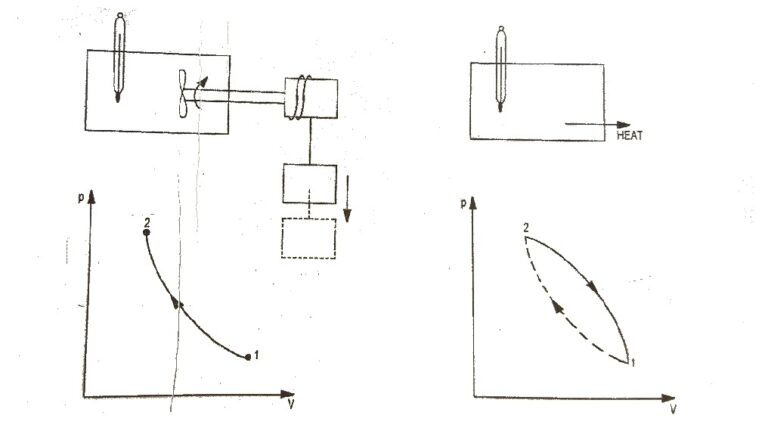
First Law of a Closed System Undergoing a Cycle : The first law of thermodynamics states that during any cycle a system undergoes the cyclic integral of heat is equal to the cyclic integral of the work. Fig.1 First Law of Thermodynamics To illustrates this, consider the gas as a system in…
The Sea Guardians, the maritime variant of the Predator MQ-9s are actually what that were recently inducted into the Indian Navy? Q2 – The Sea Guardians, the maritime variant of the Predator MQ-9s are actually what that were recently inducted into the Indian Navy? Answer – Drones Q1 – In the first week of December 2020, the…